Compare Rule
Using the Master Rule, the logical connection between the core entities in the two applications has been established. Next we need to compare in more detail. The Compare Rule defines attributes of these objects and the comparison logic which is used to compare the values (an exact comparison or a variety).
If the objects fulfill the Compare rule, the relevant information is generated to the Compare results Catalog; otherwise an error or mismatch is reported.
Compare Rule Definition
Defining a Compare Rule enables you to recognize similar pieces of equipment (CPU, Monitor...etc. in each application).
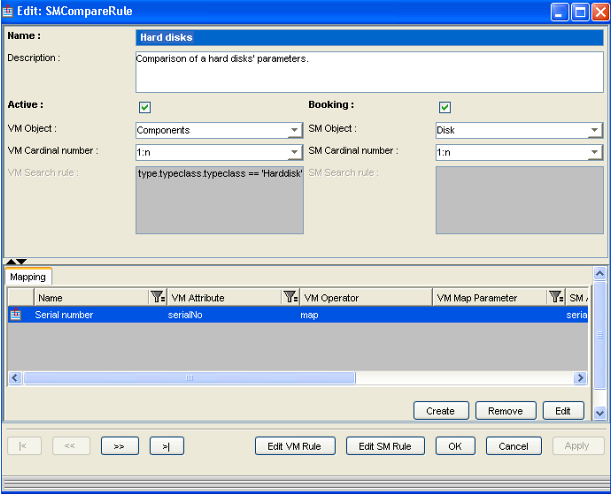
In this example, the compare rule specifies how to recognize a Hard Disk in each application. In Valuemation, this is recognized if the TypeClass in the associated Type contains the text “Harddisk”. In CIC, we directly look for SM Object Type "Disk".
Window Component |
Function / Meaning |
Name |
Name of the Compare rule. |
Description |
More detailed description of the rule. |
Active |
If the checkbox is selected, the Compare Rule is active. More than one rule can be active at any time. All active Compare Rules are used to compare the Valuemation and Systems management information. |
Booking |
If the checkbox is selected, the Compare Process will not use the field in any comparison if it has already been successfully matched. This means if one attribute of the VM Object has been successfully matched to a corresponding SM Object attribute, the attribute is no more used for any comparison. If the Booking checkbox is not selected, one attribute can be successfully compared to other attributes more than once. |
VM Object |
Specifies a class of compared objects (e.g. component, person, system...) on Valuemation side. A list of Valuemation business object types is offered for selection. |
SM Object |
Specifies a class of compared objects (e.g. Disk, Memory, CPU...) on the external system side (CIC). |
VM Cardinal number |
Specifies a range of allowed instances of objects on the Valuemation side. |
SM Cardinal number |
Specifies a range of allowed instances of objects on the external system side. |
VM Search rule |
Specifies a condition which is applied to the VM objects (named above). This isolates equipment of a specific type. The detailed comparison (Mapping) is applied only to the instances which fulfill the rule. This field is not editable. Use the Edit VM Rule at the bottom of the screen. The syntax is the Valuemation syntax for defining conditions. |
SM Search rule |
Specifies a condition which is applied to the SM objects (named above). This isolates equipment of a specific type. The detailed comparison (Mapping) is applied only to the instances which fulfill the rule. This field is not editable. Use the Edit SM Rule at the bottom of the screen. |
Mapping |
Defines attributes of a piece of equipment and the way of comparison (see also Mapping /Map Operator). |