System
Object type System represents a collection of components that is used at a particular location to fulfill a certain task.
The position of a system in the overall infrastructure environment is defined by its relations to other objects.
- Components
A system usually consists of (has links to) multiple components. A system may have only one component or no component at all. The system's components are administered in the 'Components Installed' section of the system editor.
- User(s)
A system can be assigned to one or more persons. A system can also be registered without a person assignment. The persons assigned to the system are administered in the 'Persons' section of the system editor.
Traditionally (e.g. in the IMAC actions) the assigned persons are referred to as 'users'. It is, however, possible to specify different roles of the assigned person: Owner, System Maintenance, System Supporter, System Manager. This role assignment is also handled in the 'Persons' section.
- Location
Location represents the physical placement of the system, it points to an existing object of the Location-Room object type. At a given point of time, a system must be assigned to just one location. As with most of these relations, the assignment is time-related which makes it possible to track past system locations if necessary. Location assignments are administered in the 'Location' section of the system editor, the 'All-Historical-Current' drop down button at the right of the catalog can be used to select the respective view mode.
- Organization Unit
Organization unit represents the company department to which the system belongs from the organizational point of view. A system can be assigned to zero or one organization unit (department). Organization unit assignments are administered in the 'Organization Unit' section of the system editor.
- Cost Center
Cost center represents the system's filing from the financial/accounting point of view. A system must be assigned to at least one cost center. Cost center assignments are administered in the 'Cost Centers' section of the system editor.
- Usage Types
Usage types describe the intended use of the system. A system must have at least one usage type assigned, multiple usage types of one system are possible. Usage type assignments are administered in the 'Usage Types' section of the system editor.
The above listed system relations are either mandatory or at least considered for all systems. All of them are also time-related in the sense explained in the 'Location' paragraph. Depending on business requirements, additional assignments can be used:
- Services - services which the system uses, Used by Services - services which use the system as their resource
- Contract Items, Request Items - link to the Contract and Service Request Management
- Tickets - link to the Incident/Problem/Change functionality
- Reservations - link to Resource Management
- Network - objects registering network-related information
- System Measures - objects used to plan long and short term strategies for administration of a particular system
- Documentation - objects containing additional information and attachments relevant to the system
- Expected Changes - objects documenting changes to the system
These assignments are administered in respective editor sections. Use the sections selector in the upper left-hand corner of the System editor to display or hide individual sections as needed.
System Classification
Consistency in the Asset processes is supported by mandatory system categorization at two levels:
- System Type
System Type represents technical categorization of systems.
- System Class
System Classes further classify System Types.
Examples:
- System types 'Workstation Desktop MAC', 'Workstation Desktop UNIX', 'Workstation Notebook MAC', 'Workstation Notebook Windows', etc. belong to the 'IT_Workplace' system class.
- System types 'SW Pool', 'Stock Booked Out' and 'HW Stock' belong to the 'IT_Stock' system class.
This grouping of system types with similar characteristics is used to control the availability of dynamic GUI elements. System class attributes 'Asset relevant' and 'CMS relevant' enable categorization of system types according to their field of relevance (asset stock management or configuration management). Similarly, Configuration Item Relation Definitions defined at the level of system types specify standard relations of systems of the given system type to other object types.
Functionally, the two levels of classification should be sufficient to ensure a workable systems structure. For example, several stock system types of the Stock system class can be used as repositories of unused components, different ones or software, hardware etc.
The components stored for re-use retain their item/item type relation. This relation provides the components with licensing information relevant to their lawful re-use (harvested for re-use, re-allocated, end-of-license removal...).
System Status
Individual phases of the system life cycle are marked by system statuses. Strictly defined set of statuses and status transitions ensures adherence to standard company processes. See 'System Status Diagram'.
System Editor
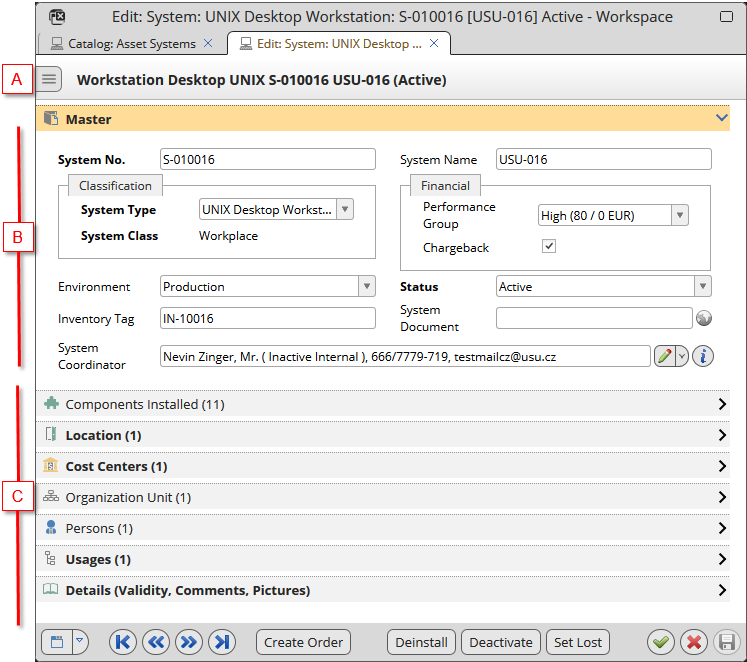
System Editor: A - sections selector B - main system attributes in the Master section C - sections with system relations