Example: N:M Relationship
An example of a straightforward m:n relationship is the System: Usage Type. A System can be used in many different ways. A usage type may be referred to in many different systems.
For the relation between Systems and Usage Types, a new table is required where Systems and Usage types are allocated to one another. The primary key of this new table is the combination of the Systems and UsageTypes. This table defines the relation between Systems and Usage Types.
- First, the two partial relations must exist
The System business object has a relation to the SystemUsageType relation table, and the UsageType business object also has a relation with the SystemUsageType relation table. These must be defined first.
- Second, the composite M:N Relation is created
To create a new m:n relation type, click the “N:M Relation” button on the Relation window and a new "n:m" Relation Customizer dialog box appears. Here the composite N:M relation is defined.
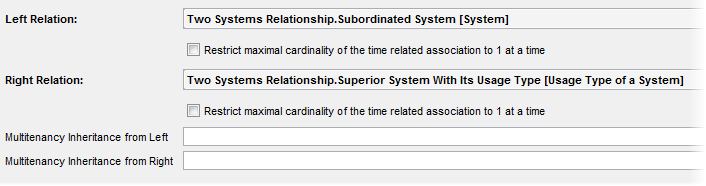
To Define an n:m relation:
- Select the two relations from the combo boxes.
- Decide if you want to restrict maximal cardinality of the time related association to 1 at a time.
This function is coupled with time-related relation. This is not required for Systems and Usage Types so it is left unchecked here.
You can also set the Multitenancy Inheritance. This option relates to the Multitenancy Inheritance as a feature of the Multitenancy functionality. Please see the dedicated Multitenancy section for overall explanation.
Now save a new n:m relation by clicking the 'Save' button. If you open the Relation main window again, you can find this new "System - Usage" m:n relation in the list of relations.