Translations Hierarchy
Object type and attribute translations behave in the following way:
- Object type/attribute translations form a hierarchy with 'Particular' at the top and 'No Specialization' at the bottom of priorities.
- English is used as a fall-back language. If no translations for the currently used language exist, the corresponding type of English translation is used.
- If even English translations are missing, the attribute name without translation is used.
Translations Hierarchy Graphically:
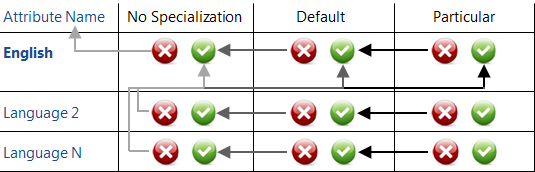
- If a 'Particular' translation exists for a given element in the selected language, it is used. If no 'Particular' translation exists, the 'Default' translation is used. If no 'Default' translation exists, the 'No Specialization' translation is used.
- If no translation of any type exists for a given element in the selected language, the English translation of the matching type is used. If the corresponding English translation does not exist, the English translation next in the hierarchy is used.
- If even the 'No Specialization' English translation is missing, the actual name of the attribute is used.
Examples
Example 1:
- Languages: English and German
- Element: attribute 'Name' of the 'System' object type
- Existing translations: English 'No Specialization', English 'Default - catalog', English 'Particular - for the displayed catalog', German 'No Specialization'
- GUI situation: current GUI language - German, a particular catalog of the object type displayed.
The translation to be used for the 'Name' attribute in the catalog results from the following hierarchy:
German Particular (NO) -> German Default (NO) -> German No Specialization (YES): German No Specialization is used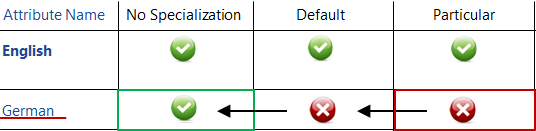
Example 2:
- Languages: English and German
- Element: attribute 'Name' of the 'System' object type
- Existing translations: English 'No Specialization', English 'Default - catalog', English 'Particular - for the displayed catalog'
- GUI situation: current GUI language - German, a particular catalog of the object type displayed.
The translation to be used for the 'Name' attribute in the catalog results from the following hierarchy:
German Particular (NO) -> German Default (NO) -> German No Specialization (NO) -> English Particular (YES): English Particular translation for the displayed catalog is used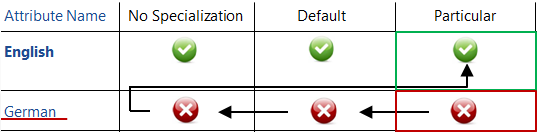
Example 3:
- Languages: English, German and Italian
- Element: attribute 'Name' of the 'System' object type
- Existing translations: English 'No Specialization', English 'Default - catalog', English 'Particular - for a catalog different from the currently displayed', German 'No Specialization', German 'Default - catalog', German 'Particular - for the displayed catalog'
- GUI situation: current GUI language - Italian, a catalog with particular translation for the attribute existing only in German is displayed.
The translation to be used for the 'Name' attribute in the catalog results from the following hierarchy:
German Particular (NO) -> German Default (NO) -> German No Specialization (NO) -> English Particular (YES, but not for the currently displayed catalog) -> English Default (YES): English Default translation for catalogs is used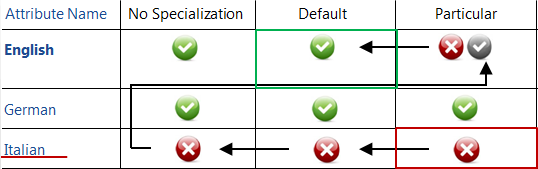
Tooltips
Note that not only translations but also tooltips behave in the same way. This means that the Translation Editor can be used do create specific tooltips for attributes according to the context. For example, one and the same attribute may require different instructions in the context of different editors.